Prostate health is a significant concern for men, particularly as they age. While genetics play a role in the risk of developing prostate issues such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and prostate cancer, lifestyle factors can also have a profound impact. Adopting healthy lifestyle changes can help maintain prostate health and potentially reduce the risk of prostate-related diseases. This article outlines key lifestyle changes that can support prostate health.
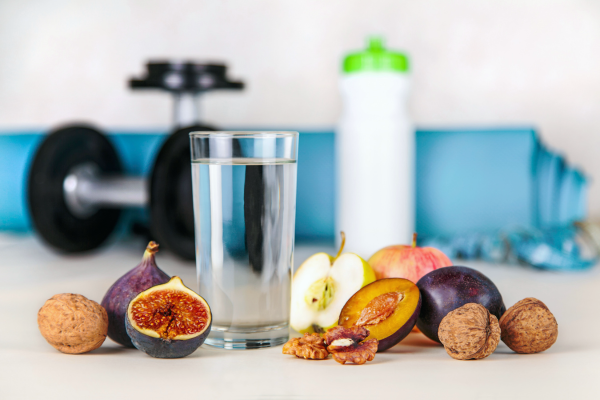
Diet and Nutrition
- Balanced Diet:
- Description: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential for overall health, including prostate health.
- Benefits: Consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods provides antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support prostate function and reduce inflammation.
- Healthy Fats:
- Description: Incorporating healthy fats from sources like fish, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- Benefits: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, have anti-inflammatory properties and may reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
- Cruciferous Vegetables:
- Description: Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts.
- Benefits: These vegetables contain compounds like sulforaphane that have been shown to protect against cancer.
- Tomatoes and Lycopene:
- Description: Tomatoes and other red fruits contain lycopene, a powerful antioxidant.
- Benefits: Lycopene has been associated with a lower risk of prostate cancer.
Physical Activity
- Regular Exercise:
- Description: Engaging in moderate to vigorous physical activity most days of the week.
- Benefits: Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces inflammation, and improves immune function, all of which can protect against prostate disease.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises:
- Description: Exercises that strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
- Benefits: These exercises can improve urinary control and reduce symptoms of BPH and prostatitis.
Weight Management
- Healthy Weight:
- Description: Maintaining a healthy body weight through diet and exercise.
- Benefits: Obesity is a risk factor for prostate cancer and other prostate issues. A healthy weight reduces this risk.
- Avoiding Excessive Caloric Intake:
- Description: Monitoring and controlling portion sizes and caloric intake.
- Benefits: Prevents weight gain and obesity, contributing to better prostate health.
Hydration
- Adequate Hydration:
- Description: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Benefits: Proper hydration supports urinary function and helps flush out toxins that can affect the prostate.
Avoiding Risk Factors
- Limiting Alcohol and Caffeine:
- Description: Reducing intake of alcohol and caffeinated beverages.
- Benefits: Excessive alcohol and caffeine can irritate the bladder and worsen urinary symptoms.
- Avoiding Smoking:
- Description: Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke.
- Benefits: Smoking is linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer and other health issues.
Stress Management
- Managing Stress:
- Description: Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing.
- Benefits: Chronic stress can negatively impact immune function and overall health, including the prostate.
Regular Health Screenings
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test:
- Description: Regular PSA screenings as recommended by healthcare providers.
- Benefits: Early detection of prostate issues can lead to better outcomes and more effective treatment.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE):
- Description: Regular DREs to check for prostate abnormalities.
- Benefits: Allows for early detection of prostate enlargement or irregularities.
Conclusion
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in maintaining prostate health and reducing the risk of prostate-related diseases. A balanced diet, regular exercise, weight management, adequate hydration, avoiding harmful substances, managing stress, and regular health screenings are essential components of a proactive approach to prostate health. By making these positive changes, men can improve their overall well-being and support the long-term health of their prostate.
References
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2020). Prostate cancer prevention: Ways to reduce your risk. Retrieved from Harvard Health
- National Institute on Aging. (2017). Prostate changes and aging. Retrieved from NIA
- American Cancer Society. (2021). Nutrition and physical activity guidelines for cancer survivors. Retrieved from American Cancer Society
- Mayo Clinic. (2020). Prostate cancer prevention: Ways to reduce your risk. Retrieved from Mayo Clinic
- World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research. (2018). Diet, Nutrition, Physical Activity and Prostate Cancer. Retrieved from WCRF/AICR